XML SiteMap Vs HTML SiteMap Which is Right for Your Website?
In the ever-evolving landscape of website optimization and search engine visibility, understanding the roles and benefits of XML Sitemaps and HTML Sitemaps is crucial.
In this blog post, we will take a closer look at:
- What is XML Site-Map
- Benefits of XML Site-Map
- What is HTML Site-Map
- Difference between XML SiteMap and HTML SiteMap
- How to Create and Submit Your SiteMap to Google Search Console
XML Site-Map XML Sitemaps: Guiding Search Engine Robots
What is an XML Sitemap?
An XML Sitemap is used for search engine robots. XML sitemap is written mainly for search engines. In XML sitemap we tell search engines of all our website pages, we have chosen to tell search engines to index. It serves as a roadmap of your website’s structure, listing the URLs of important pages you want search engines to crawl and index. This helps search engines understand the organization of your site, ensuring they don’t miss any valuable content.
In other words, XML sitemaps tell search engines which are important pages of the website.
Search engine like Google often uses the sitemap file as a guide to the pages available on your website, however, it is not necessary, for a search engine to index every page you list on your sitemap.
Benefits of XML Site-Map”
A sitemap can improve the crawling of your site, and helpful for :
- Large Websites: Navigating extensive websites can be challenging for search engine bots. XML Sitemaps facilitate their crawl by providing a clear outline of your site’s architecture.
- New Websites: For new sites, search engines might not yet have discovered all your content. XML Sitemaps ensure prompt indexing of your pages.
- Content Duplication: XML Sitemaps can indicate when content was published, aiding in managing content duplication concerns.
- Pages with Poor Linking: If some pages aren’t well-linked within your site, an XML Sitemap can help search engines find and index them.
XML sitemap can also helps to handle content duplication issues. The sitemap will show the date the content was published, in this way you show to search engine that you are an original content creator.
It helps search engine robots to read and crawl your site more effectively. It is very difficult for humans to read XML sitemap.
HTML Sitemaps: Enhancing User Navigation
What is an HTML Sitemap?
HTML Site-Map – are written for humans. – An HTML sitemap helps human users to find a page on your site that they are looking for. if any user is not able to find a specific page on the website then he can make use of the HTML site map and easily access that page.
In this way, we can provide a user-friendly website and a better user experience by providing an HTML sitemap. And by providing a better user experience, you may improve your site’s ranking.
Difference between XML SiteMap and HTML SiteMap
There is no risk, associated with a sitemap, it provides only benefits for your website.
Both XML and HTML sitemaps help search engines crawl your site.
HTML Sitemaps: Enhancing User Navigation
What is an HTML Sitemap?
Unlike XML Sitemaps, HTML Sitemaps are designed for human users. HTML Sitemaps are designed mainly to help website visitors for better understanding of our website. It helps human users to find web-page pages on your website easily.
On the other hand, XML Site-Map is written mainly for search engine to crawl your site more effectively.
I hope, you have understood difference between XML Site-Map and HTML Sitemap.
Benefits of HTML Sitemaps:
HTML Sitemaps contribute to a positive user experience and better site performance by:
• Improved User Navigation: When visitors can’t find a specific page through regular navigation, an HTML Sitemap provides an easy-to-use backup.
• Enhanced Accessibility: HTML Sitemaps make your content accessible to users who might not navigate your site in the conventional manner.
• User Experience Boost: A well-structured HTML Sitemap showcases your commitment to user experience, potentially leading to higher engagement and conversions.
Key Differences Between XML Sitemaps and HTML Sitemaps
| Aspect | XML Sitemap | HTML Sitemap |
| Audience | Search Engine Robots | Human Visitors |
| Purpose | Assist in Crawling and Indexing | Improve User Navigation |
| Content | URLs and Metadata | Links to Pages |
| Visibility | Not Visible to Users | Visible as a Web Page |
| Crawling Emphasis | Search Engine Bots | User-Friendly Links |
How to Create XML SitemMap & Submit to Google Search Console
Watch Video If You Prefer to See Video :
How to create and submit your sitemap to Google Search Console
Before you upload sitemap to Google Search Console you need to do two important things:-
- Create you XML SiteMap File (2) upload your SiteMap.xml file to the roo directory of your website
And Last Step >>> Submit sitemap url to Google Search Console.1. Create your sitemap XML file>>>
Create your sitemap XML file through XML-sitemaps.com and download SiteMap.XML file to your Desktop.
Upload your sitemap.xml file to the root directory of your website.
Steps for upload sitemap.xml file to the root directory of website :-
Step a) login to C-Panel of your website
Step b) Click on File Manager
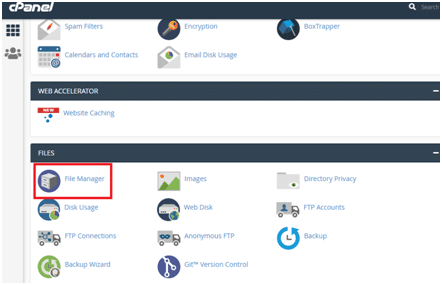
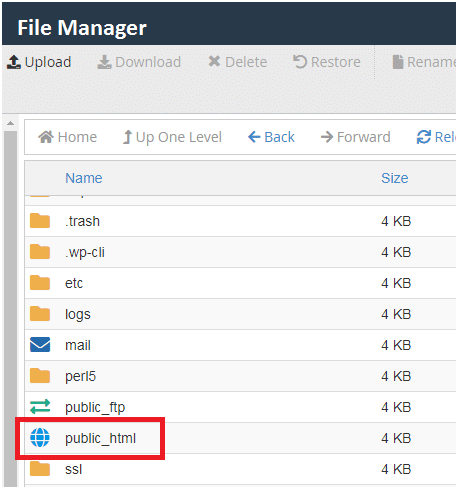
Step c) Double click on public_html
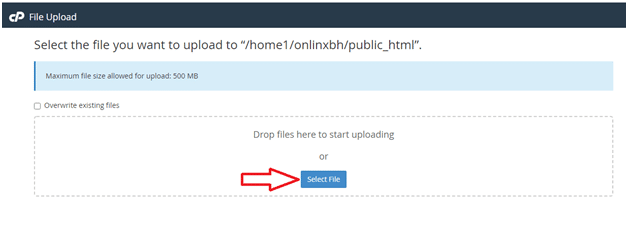
Step d) Click on Upload button and click “Select File”button and upload “Sitemap.XML”from your computer.
Steps for submit your sitemap to Google Search Console
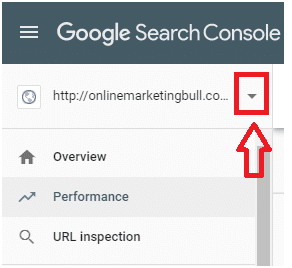
- Sign in to Google Search Console.
- In the sidebar, select your website.

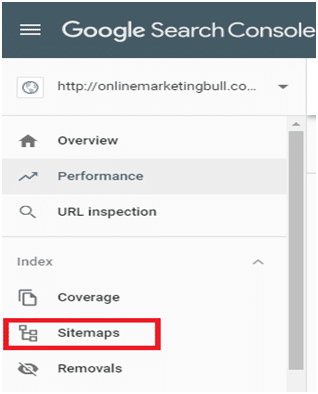
- Click on ‘Sitemaps’. You need to click on ‘Sitemaps’ menu is under the ‘Index’ section.

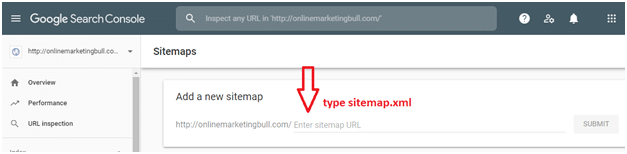
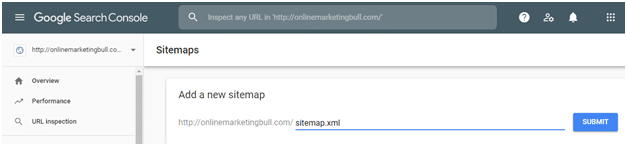
- Enter “sitemap.xml” in the ‘Add a new sitemap’ field to complete the sitemap URL.


- Click Submit.In conclusion, both XML and HTML Sitemaps are valuable tools in your website optimization arsenal. XML Sitemaps aid search engines in understanding your site’s structure, while HTML Sitemaps enhance user navigation and experience. By utilizing both, you can strike a balance between catering to search engines and providing a seamless experience for your visitors.Remember, as technology evolves, staying informed and adapting your strategies accordingly is key to maintaining a strong online presence.